Introduction to Abaqus FE program
Abaqus is a software suite for finite element analysis and computer-aided engineering, originally released in 1978. The name of this software are based on the abacus calculation tool.
Abaqus is a suite of powerful engineering simulation programs, based on the finite element method, that can solve problems ranging from relatively simple linear analyses to the most challenging nonlinear simulations. ABAQUS contains an extensive library of elements that can model virtually any geometry. It has an equally extensive list of material models that can simulate the behavior of most typical engineering materials including metals, rubber, polymers, composites, reinforced concrete, crushable and resilient foams, and geotechnical materials such as soils and rock. Designed as a general-purpose simulation tool, ABAQUS can be used to study more than just structural (stress/displacement) problems. It can simulate problems in such diverse areas as heat transfer, mass diffusion, thermal management of electrical components (coupled thermal-electrical analyses), acoustics, soil mechanics (coupled pore fluid-stress analyses), and piezoelectric analysis.
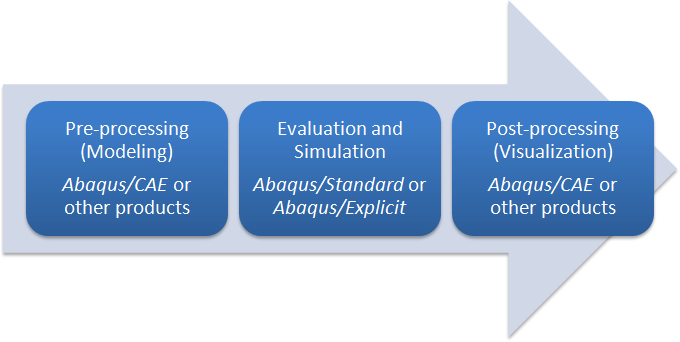
The Abaqus product suite consists of five core software products
Computer-Aided Engineering It is a software application used for both the modeling and analysis.
Abaqus/Standard a general-purpose Finite-Element analyzer that employs implicit integration scheme (traditional).
Abaqus/Explicit a special-purpose Finite-Element analyzer that employs explicit integration scheme to solve highly nonlinear systems.
Abaqus/CFD a Computational Fluid Dynamics software application which provides advanced computational fluid dynamics capabilities..
Abaqus/Electromagnetic a computational electromagnetics software application which solves advanced computational electromagnetic problems
Workflow

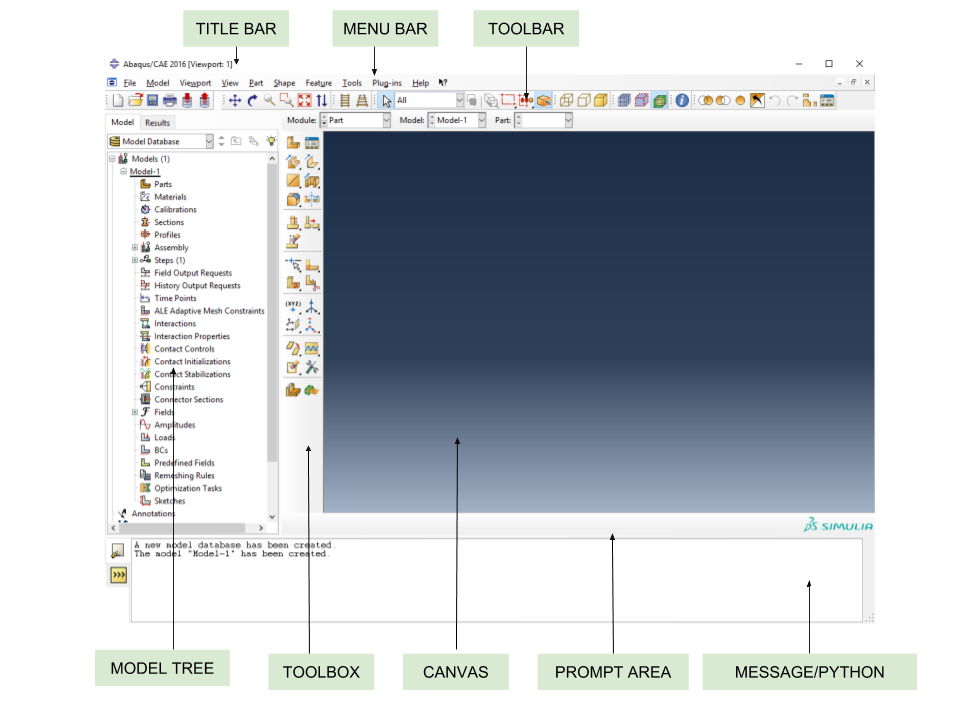
Abaqus/CAE modules
Part - Sketch a two-dimensional profile and create a part representing the object.
Property - Define the material properties and other section properties of the part.
Assembly - Assemble the model.
Step - Configure the analysis procedure and output requests.
Load - Apply loads and boundary conditions to the parts.
Mesh - Mesh the parts.
Job - Create a job and submit it for analysis.
Visualization - View the results of the analysis.
ABAQUS CAE
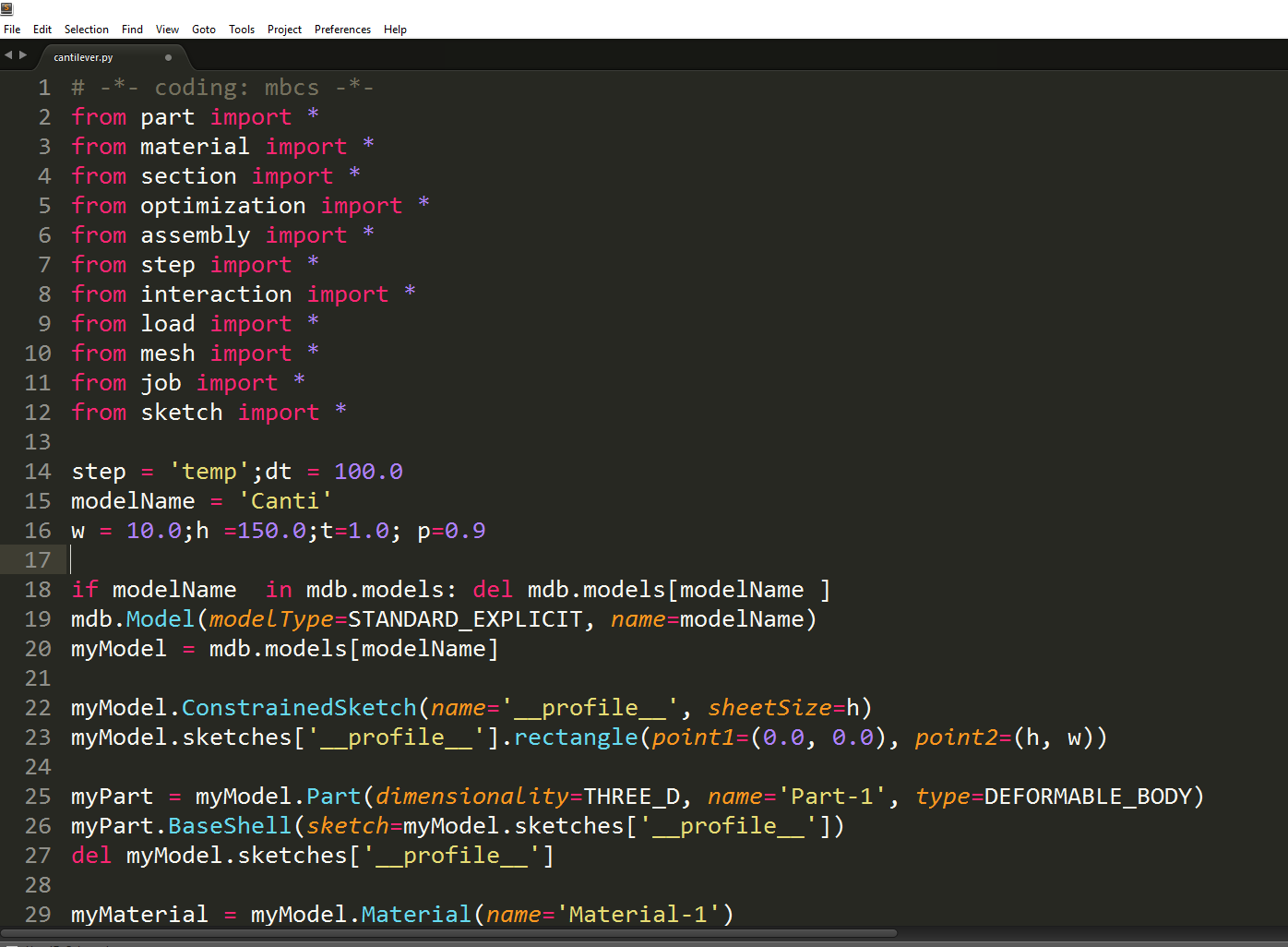
Python Scripts for Abaqus
Python scripts let you accomplish tasks in Abaqus that would be time consuming or practically impossible in the GUI (Abaqus/CAE). Using a script you can automate a repetitive task, vary parameters of a simulation as part of an optimization study, extract information from large output databases.
Input file
The input file is the means of communication between the preprocessor, usually ABAQUS/CAE, and the analysis product, ABAQUS/Standard. It contains a complete description of the numerical model. The input file is a text file that has an intuitive, keyword-based format, so it is easy to modify using a text editor if necessary; if a preprocessor such as ABAQUS/CAE is used, modifications should be made using it. Indeed, small analyses can be specified easily by typing the input file directly.
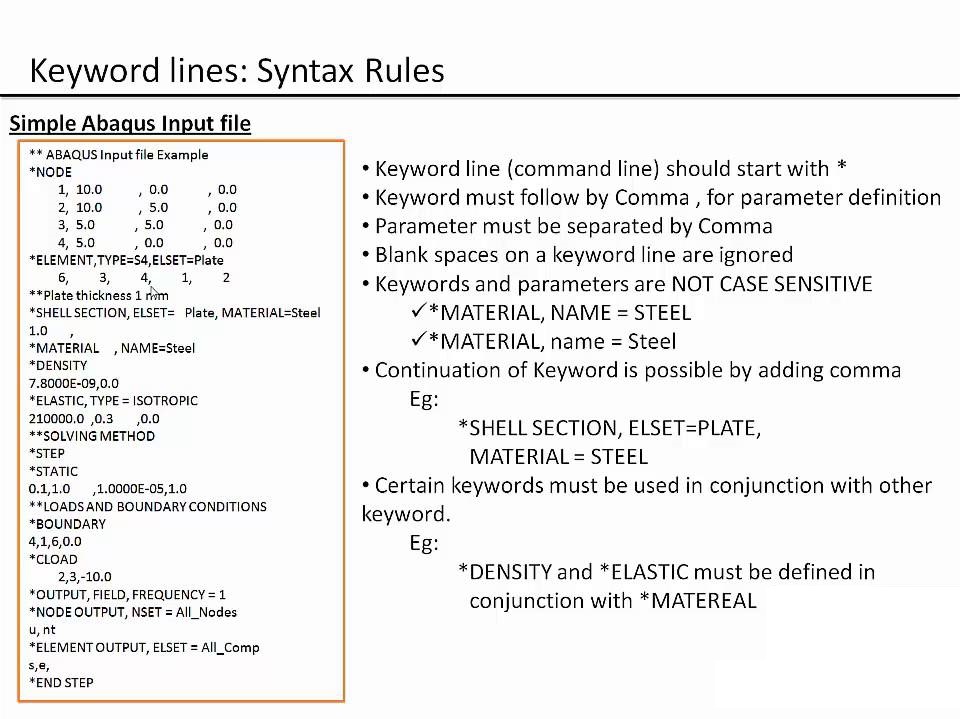
The input file is composed of a number of option blocks that contain data describing a part of the model. Each option block begins with a keyword line, which is usually followed by one or more data lines. These lines cannot exceed 256 characters.
Units
Before starting to define any model, you need to decide which system of units you will use. ABAQUS has no built-in system of units.
| Quantity | SI | SI (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| Length | m | mm |
| Force | N | N |
| Mass | kg | tonne (10$^{3}$kg) |
| Time | s | s |
| Stress | Pa (N/m$^2$) | MPa (N/mm$^2$) |
| Energy | J | mJ (10$^{-3}$J) |
| Density | kg/m$^3$ | tonne/mm$^3$ |